Setting Up a Data Lake for ERP: A Comprehensive Guide:
Introduction:
In today’s digital era, ERP systems are crucial for managing business operations. However, the vast amount of data generated can be overwhelming. To harness the full potential of your ERP data, setting up a data lake is the solution. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of creating a robust data lake for ERP while optimizing for search engines.

Understanding Data Lakes for ERP:
- What is a Data Lake?
A data lake is a central repository that allows organizations to store, manage, and analyse vast amounts of structured and unstructured data at scale. It’s a flexible storage solution that can accommodate diverse data types, such as text, images, videos, and more. - Why Your ERP Needs a Data Lake:
ERP systems generate massive volumes of data, including transactional data, financial records, supply chain data, and more. Storing this data in a data lake ensures that it can be efficiently managed, accessed, and analysed for valuable insights. - Benefits of Data Lakes for ERP:
Data lakes provide benefits like scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to support real-time data processing. They enable organizations to perform advanced analytics, uncover trends, and make data-driven decisions. - Challenges and Considerations:
While data lakes offer many advantages, they also come with challenges, including data quality issues, security concerns, and the need for effective data governance. Considerations such as data security and privacy regulations are crucial in the planning process.
Planning Your Data Lake Strategy:
- Designing Your Data Lake Architecture:
This section delves into the architectural aspects of a data lake. It discusses different data lake architectures, including centralized, decentralized, and hybrid approaches. Factors like data volume, variety, and velocity are considered when designing the architecture. - Data Governance Best Practices:
Effective data governance is critical for maintaining data quality and ensuring compliance with regulations. Topics covered include defining data ownership, establishing data stewardship, and creating data governance policies. - Data Lake Security Measures:
Data lake security is a paramount concern. The chapter outlines security measures, including encryption, access control, and monitoring, to safeguard data stored in the data lake. - Scalability and Performance:
Scalability is key to accommodating growing data volumes. The chapter discusses strategies for scaling your data lake infrastructure and optimizing performance.
Work-flow Diagram for Oracle Fusion, Snowflake and Data Lake ERP process:
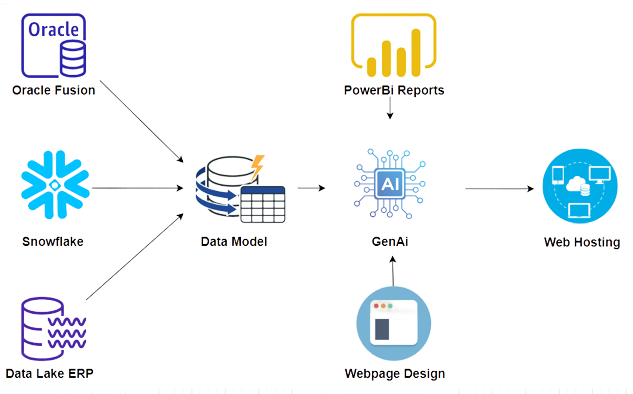
Data Ingestion and Storage:
- Data Ingestion Methods:
This section covers various methods for ingesting data into the data lake, such as batch processing, real-time streaming, and Change Data Capture (CDC). - Choosing the Right Storage Technology:
The choice of storage technology impacts data retrieval and analysis. Common technologies like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), cloud-based storage solutions, and object storage are discussed. - Data Lake File Formats:
Different file formats like Parquet, Avro, ORC, and JSON offer various advantages. This chapter explains the benefits of each format and helps you choose the most suitable one for your data lake.
Data Cataloguing and Metadata:
- Creating a Data Catalog:
A data catalog is a crucial component for data discovery and management. This section explains how to create a comprehensive data catalog that includes metadata, data lineage, and data definitions. - Metadata Management Best Practices:
Effective metadata management ensures that data is well-documented and easily searchable. Best practices for metadata creation, maintenance, and integration are covered. - Data Lineage and Tracking:
Understanding data lineage is essential for tracking the origin and transformations of data within the data lake. This chapter describes methods for establishing and maintaining data lineage

Data Transformation and Processing:
- ETL Processes in a Data Lake:
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes are essential for preparing data for analysis. This section explores ETL strategies, tools, and frameworks tailored to data lakes. - Data Transformation Tools and Frameworks:
Common tools and frameworks for data transformation, such as Apache Spark and Apache Flink, are discussed, along with their use cases. - Real-time Data Processing:
Real-time data processing capabilities are crucial for timely insights. Topics include stream processing, event-driven architectures, and Lambda and Kappa architectures.

Data Analytics and Insights:
- Leveraging Analytics Tools:
This chapter introduces analytics tools like Power BI, Tableau, and Apache Superset for visualizing and analysing data in the data lake. - Generating Business Insights:
Discover how to derive actionable insights from your data by applying analytics techniques, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. - Data Lake Querying and SQL Support:
Learn how to perform SQL queries on data lakes using query engines like Apache Hive, Apache Presto, and AWS Athena.
Data Lake Maintenance and Optimization:
- Regular Data Lake Maintenance Tasks:
This section covers routine maintenance tasks such as data quality checks, data pruning, and system monitoring to ensure the data lake operates smoothly. - Performance Optimization Strategies:
Explore strategies for optimizing the performance of your data lake, including partitioning, indexing, and query optimization. - Cost Management and Scaling:
Efficiently manage costs associated with your data lake, including cloud storage costs, by implementing cost-effective scaling and resource management strategies.
Conclusion:
1. Setting up a data lake for ERP is a strategic move to unlock the full potential of your enterprise data. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish a robust data lake that ensures data accessibility, security, and valuable insights. Embrace the power of ERP data through effective data lake management.
2. This detailed guide provides valuable information about setting up a data lake for ERP, covering various aspects from planning and architecture to data analytics and optimization.
Contact Us
Let us innovate together. If you are interested in exploring this further contact us at https://gaisolve.com/contact-us/

